41 label the glial cells of the cns
Glial Cells - Physiopedia The brain is made up of more than just neurones.Although there are about 86-100 billion neurons in the brain, there are about the same number of glial cells in the brain. Glial cells (or neuroglial cells) have a structural role within the central nervous system and also regulate nerve firing rates, brain plasticity (guiding early brain development), and immune responses. Glial Cells of the CNS - BIO 264 Anatomy & Physiology I Glial Cells of the CNS - BIO 264 Anatomy & Physiology I MODULE 6: NERVOUS SYSTEM ORGANIZATION ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Cover 1.0. MODULE 1: TERMINOLOGY/HOMEOSTASIS 1.1. TERMINOLOGY 1.1.2. Body Directions 1.1.3. Anatomical Divisions, Subdivisions and Cavities 1.1.4. Prefixes 1.1.5. Suffixes 1.1.6. Abbreviations 1.2. HOMEOSTASIS 1.2.1.
Brain Cells - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Neurons (AKA nerve cells) are the information-carrying cells of the central nervous system (CNS). They use electrical impulses and chemical signals to transmit messages between different parts of the brain, and between the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Neurons are what allow us to perceive and interact with the world around us, and ...
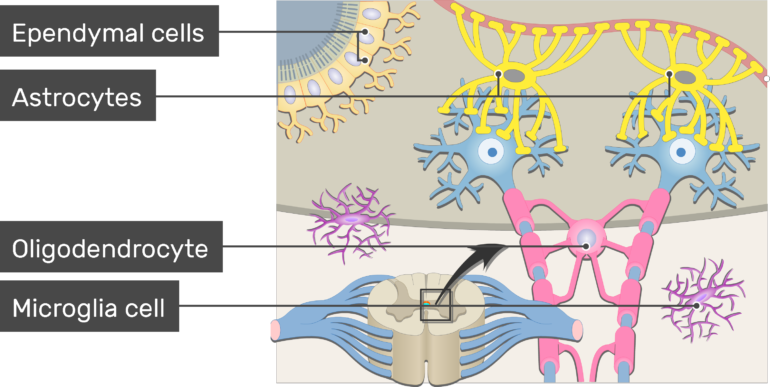
Label the glial cells of the cns
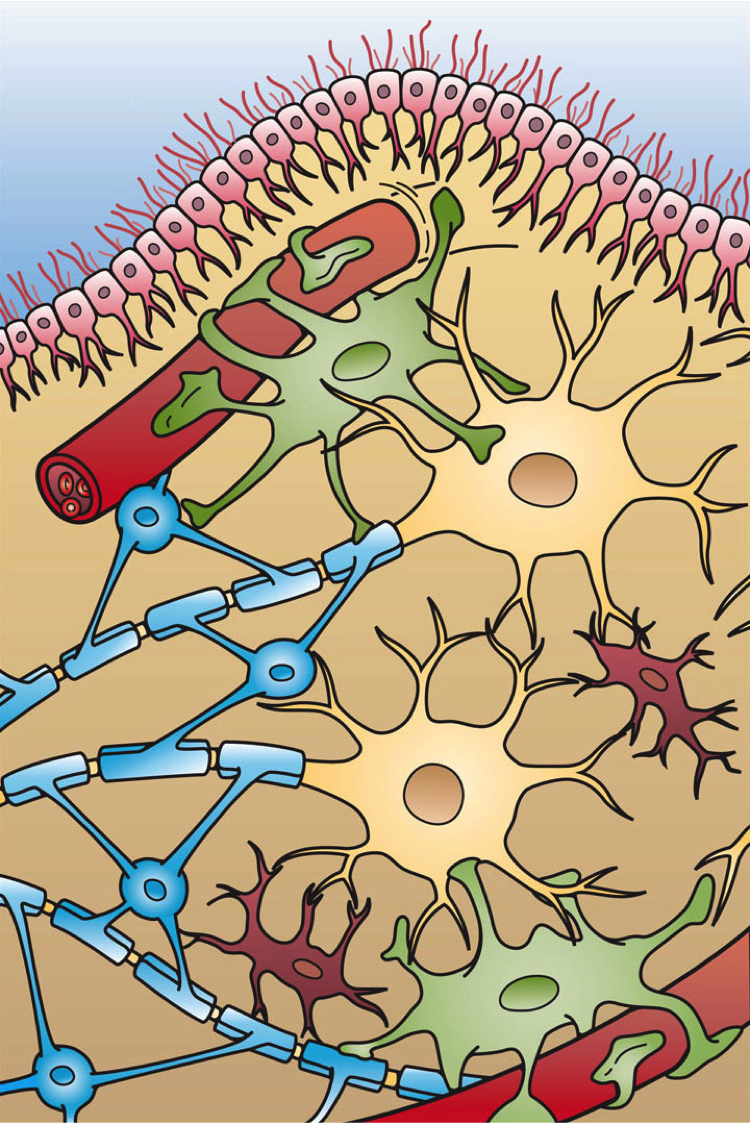
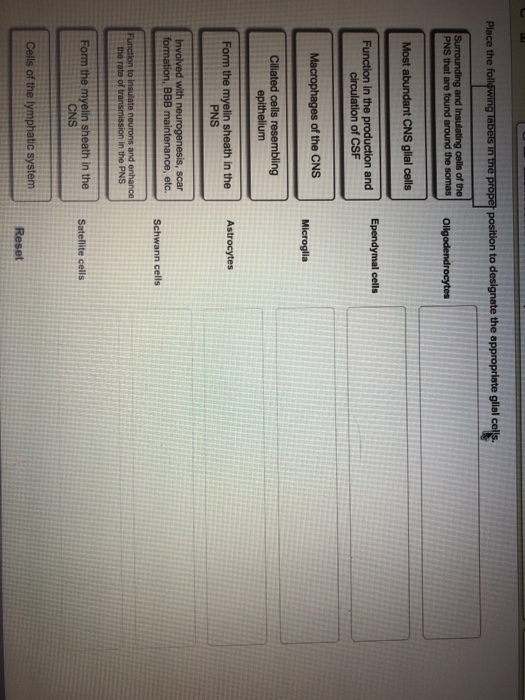
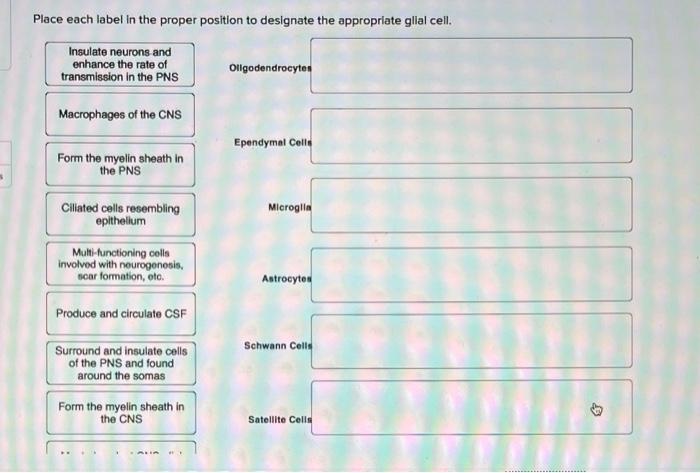
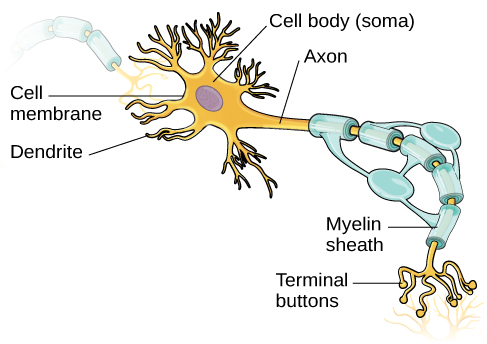
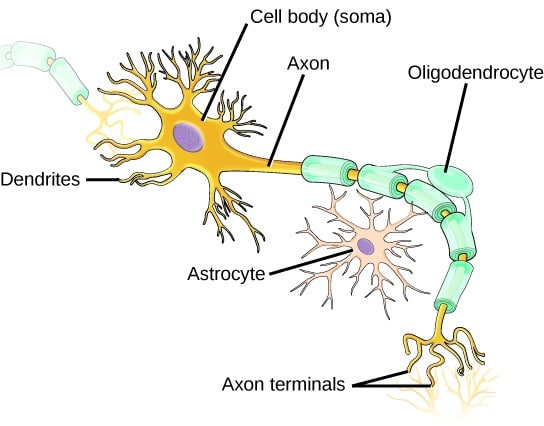
Glial Cells | Location, Structure, Summary & Function The five types of glial cells found in the central nervous system are: Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Microglia Ependymal cells Radial glia Glial cells are also found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes the nerves in the limbs that are not connected to the spine. There are two kinds of glial cells present there: Schwann cells Glial Cells - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Glial cells function as modulators of the CNS and PNS environments; they increase and decrease activity within the synapses by regulating neurotransmitter, oxygen, and ion uptake; they also aid nerve injury recovery. Specific roles are carried out by the different glial cell types. 16.1 Neurons and Glial Cells – Concepts of Biology – 1st ... Glial cells of the (a) central nervous system include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglial cells. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons. Astrocytes provide nutrients to neurons, maintain their extracellular environment, and provide structural support. Microglia scavenge pathogens and dead cells.
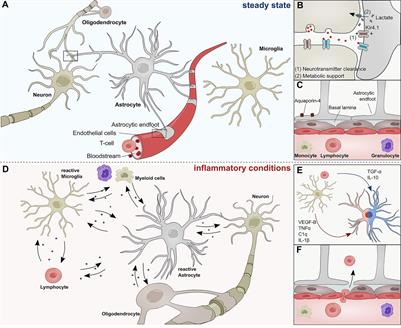
Label the glial cells of the cns. B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune disease: advances ... In spite of early successes in open-label trials, an anti-CD20 antibody ... In terms of CNS-resident B cells, ... is found on glial cells, ... Six Types of Neuroglia | Sciencing Four of them are present in the CNS: Astrocyte Oligodendrocyte Microglia Ependymal cell Two of them are present in the PNS: Satellite cell Schwann cell Satellite cells function to provide nutrients and protection to neurons in the PNS. A satellite glial cell wraps itself around the neuron's cell body. glial cells of CNS and PNS Flashcards | Quizlet four types of glial cells in CNS Astrocytes, Ependymal cells , Microglia, Oligodendrocytes stucture of astrocytes star-shaped glial cells with processes the extend from the cell body to form foot processes fuction of foot process in astrocytes cover the surface of blood vessels and neurons Astrocytes vital function formation of functional synapses Nervous System: Explore the Nerves with Interactive Anatomy … Web02.11.2020 · Myelin is formed by 2 types of glial cells: Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. In both cases, the glial cells wrap their plasma membrane around the axon many times to form a thick covering of lipids. The development of these myelin sheaths is known as myelination. Myelination speeds up the movement of APs in …
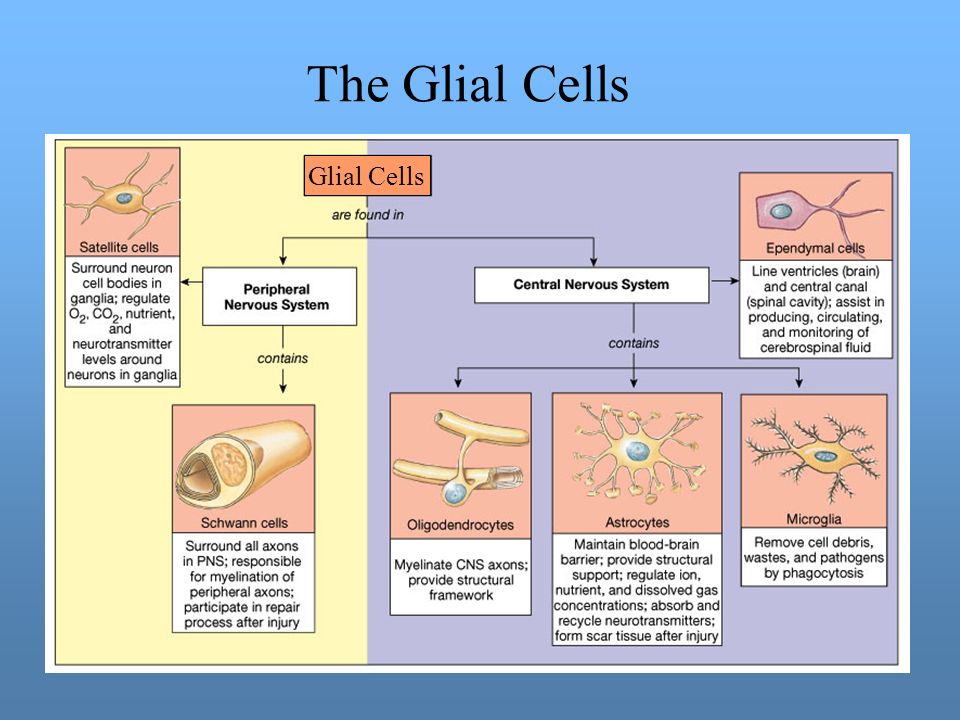
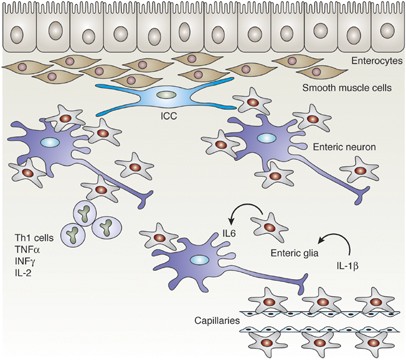
Neuronal and Glial Cell Markers | Cell Signaling Technology Upon further maturation, Schwann cells demonstrate increased expression of myelin-associated genes (e.g. myelin basic protein, MBP) to support their role as sheath-producing glial cells for PNS motor and sensory neurons. Arising from radial glial cells are intermediate progenitors, which act as a source of most mature neurons in the CNS. Histology, Glial Cells - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Many glial cells provide support for an essential nervous system function. In addition to providing support for neurons, glial cells aid in the maintenance of homeostasis, and form myelin. As a whole, glial cells are the most abundant cells in the central nervous system. The most notable glial cells include oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, astrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. Most glial ... Biosensors | Free Full-Text | Ultrasensitive Determination of Glial ... A variety of central nervous system (CNS) cell types, including astrocytes and ependymal cells, produce a glial-fibrillary-acidic-protein (GFAP), which is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein, with a molecular mass between 40 and 53 kDa . It was discovered that GFAP might be found in the blood after brain damage. What are the glial cells of the CNS and PNS? - KnowledgeBurrow.com What are the glial cells of the CNS and PNS? Glial cells are found in the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The important CNS glial cells are astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, radial glial cells, and ependymal cells. Schwann cells, enteric glial cells, and satellite glial cells are part of the PNS.
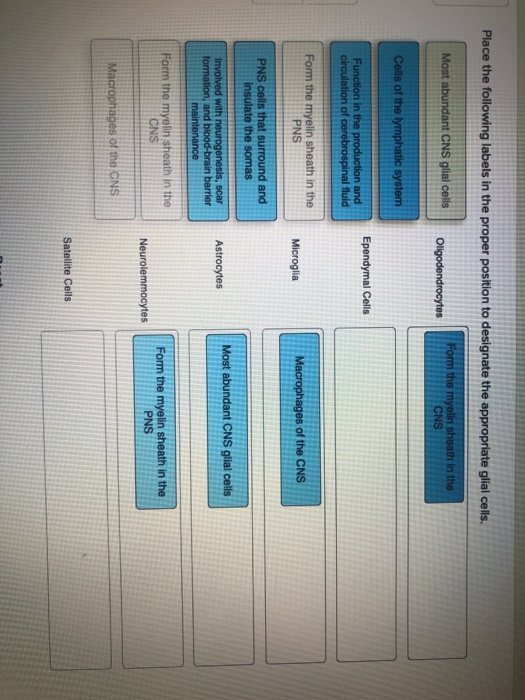
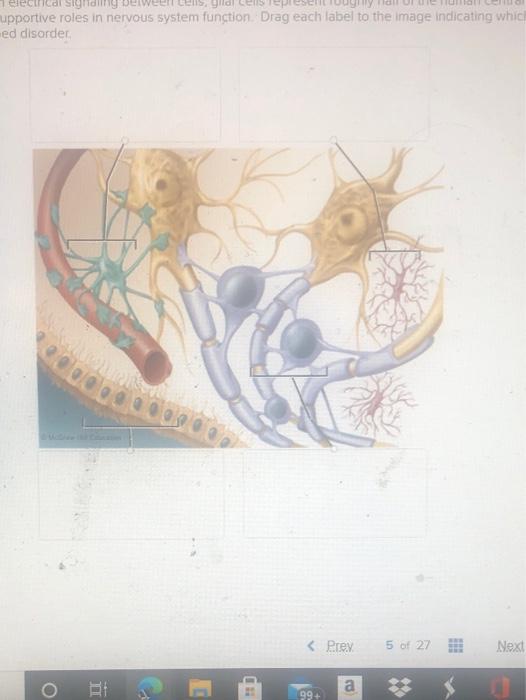
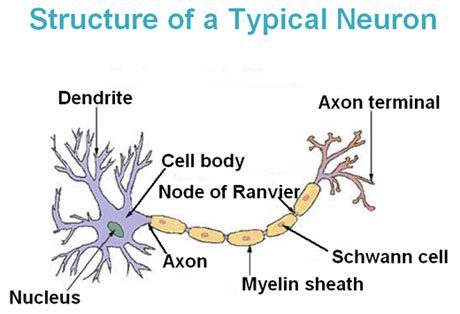
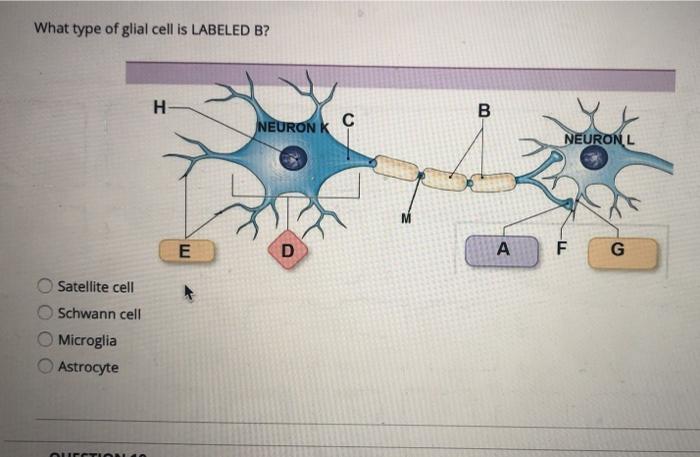
Art Labeling Activity Neuroglial Cells Of The Cns Art Labeling Activity Neuroglial Cells Of The Cns. Label art figure 87 p. ... Web some glial cells function primarily as the physical support for neurons. Human skull superior view top of cranium removed figure 511. Source: humanbiology.pressbooks.tru.ca. For each statement decide whether it is a function of the. It is neural tissue is ... Glial fibrillary acidic protein - Wikipedia WebGlial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a protein that is encoded by the GFAP gene in humans. It is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS), including astrocytes and ependymal cells during development. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in glomeruli and peritubular … LP 9 HW Flashcards | Quizlet Label the glial cells of the CNS. -Astrocyte -Ependymal Cell -Microglial Cell -Oligodendrocyte Removal of the left cerebral hemisphere would prevent voluntary movement of the right side of the body. True Place in order the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. 5 - CSF flows into the arachnoid villi and drains into the dural venous sinuses. Peripheral Nervous System | histology - University of Michigan WebThe primary differences between the CNS and the PNS are the type of glial cell that produces the myelin and the ratio of nerve fibers per glial cell. In the PNS, individual Schwann cells myelinate one internodal segment of individual axons. The oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system, however, are able to myelinate up to 50 axons each, and …
Brain (CNS) Cell Types: Neurons, Astrocytes, Microglia, Microglia are a cell type, that is only found in the CNS (Central Nervous System; per human definition: brain and spinal cord). Usually microglial cells are in a so called ramified state, in which they are immunologically inactive. However they can be " activated " via various triggers (all caused by some kind of brain injury):
4.2: Neurons and Glial Cells - Biology LibreTexts Glial cells of the (a) central nervous system include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglial cells. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons. Astrocytes provide nutrients to neurons, maintain their extracellular environment, and provide structural support. Microglia scavenge pathogens and dead cells.
Radial glial cells: key organisers in CNS development - PubMed Radial glia are elongated bipolar cells present in the CNS during development. Our understanding of the unique roles these cells play has significantly expanded in the last decade. Historically, radial glial cells were primarily thought to provide an architectural framework for neuronal migration.
Stem-cell therapy - Wikipedia WebStem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. As of 2016, the only established therapy using stem cells is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This usually takes the form of a bone-marrow transplantation, but the cells can also be derived from umbilical cord blood.Research is underway to develop various …
Ischaemic stroke | Nature Reviews Disease Primers Web10.10.2019 · Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide, and ischaemic stroke accounts for 71% of cases. This Primer by Campbell and colleagues discusses the epidemiology, mechanisms, diagnosis ...
Label the glial cells of the CNS. Ependymal cell Oligodendrocyte ... Label gital cells in the CNS by clicking and dragging the label to the correct location. Label the glial cells in the CNS by clicking and dragging the label to the correct location. Posted 7 months ago View Answer Plagiarism Checker Submit your documents and get free Plagiarism report Free Plagiarism Checker X
Retina - Wikipedia WebStructure Inverted versus non-inverted retina. The vertebrate retina is inverted in the sense that the light-sensing cells are in the back of the retina, so that light has to pass through layers of neurons and capillaries before it reaches the photosensitive sections of the rods and cones. The ganglion cells, whose axons form the optic nerve, are at the front of the …
Browse Articles | Nature Medicine Web15.12.2022 · Analyses of whole-genome sequencing data in children and validation in mouse models show that offspring born from blastocyst-stage embryo transfer have shorter leukocyte telomere lengths.
Dorsal Radial Glial Cells Have the Potential to Generate Cortical ... Human fetal brain tissue and cell culture. Human fetal brain tissue (n = 4), ranging in age from 19 to 21 g.w. (corresponding to postconceptional weeks, full term being 40 g.w.), was collected from the Human Fetal Tissue Repository at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine (Bronx, NY), after legal abortions and with proper consent from parents.The postmortem delay was, on average, 15 min.
Glial Cells: Types and Functions - Verywell Health There are five types of glial cells in your CNS: Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Microglia Ependymal cells Radial glia 1 You also have glial cells in your peripheral nervous system (PNS), which is made up of all the nerves in your body that are away from your spine (like your arms and legs). The two types of glial cells in the PNS are: Schwann cells
PubMed Journals has been shut down - NCBI Insights Jun 15, 2018 · Almost two years ago, we launched PubMed Journals, an NCBI Labs project. PubMed Journals helped people follow the latest biomedical literature by making it easier to find and follow journals, browse new articles, and included a Journal News Feed to track new arrivals news links, trending articles and important article updates. PubMed Journals was a successful … Continue reading PubMed ...
Components of the Nervous System | Biology for Majors II WebGlial Cells. While glia are often thought of as the supporting cast of the nervous system, the number of glial cells in the brain actually outnumbers the number of neurons by a factor of ten. Neurons would be unable to function without the vital roles that are fulfilled by these glial cells. Glia guide developing neurons to their destinations ...
Solved Label the glial cells of the CNS and PNS. Astrocyte | Chegg.com Question: Label the glial cells of the CNS and PNS. Astrocyte Satellite cell Microglial cell Eperdymal cell Oligodendrocyte Schwann cell This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (1 rating)
Cells of the Nervous System - Neurons - Glial Cells - TeachMePhysiology The nervous system comprises of two groups of cells, glial cells and neurones. Neurones are responsible for sensing change in their environment and communicating with other neurones via electrochemical signals. Glial cells work to support, nourish, insulate neurones and remove the waste products of metabolism.
Neuroscience For Kids - Explore the nervous system The brain contains about 86 billion nerve cells (neurons) and trillions of "support cells" called glia. The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult women and 45 cm long in adult men and weighs about 35-40 grams. The vertebral column, the collection of bones (back bone) that houses the spinal cord, is about 70 cm long.
Glial Cells Types and Functions - Simply Psychology Glial cells, also called glial cells or neuroglia, are cell which are non-neuronal and are located within the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system that provides physical and metabolic support to neurons, including neuronal insulation and communication, and nutrient and waste transport.
Glia functions in the CNS | Abcam The central nervous system (CNS) comprises a network of approximately 10 12 neurons, which mediate the transmission of action potentials. Despite the essential function of neurons, about 90% of the cells in the CNS are glia. Glia were originally believed to be passive cells that only acted physically to support neurons, hence the name glia ...
What are satellite glial cells? — Brain Stuff Satellite glial cells can be found surrounding the somata of cell bodies found in the peripheral nervous system ganglia. We have ganglia for our peripheral sensory systems, such as the somatosensory systems that detect pain or temperature. Another major component of the PNS is the autonomic nervous system, which includes the sympathetic and ...
Glial Cells | Biology for Majors II - Lumen Learning There are several different types of glia with different functions, two of which are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Glial cells support neurons and maintain their environment. Glial cells of the (a) central nervous system include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglial cells. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons.
Defining glial cells during CNS development - PubMed Defining glial cells during CNS development. Defining glial cells during CNS development Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001 Nov;2(11):840-3. doi: 10.1038/35097593. Author S C Zhang 1 Affiliation 1 Department of Anatomy and the ... Central Nervous System / growth & development
Press Releases Archive - Digital Journal Web19.12.2022 · Digital Journal is a digital media news network with thousands of Digital Journalists in 200 countries around the world. Join us!
Neuroglia Function & Tissue | Neuroglia Location in CNS - Video ... In the CNS, the most important glial cells include astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and ependymal cells. In the PNS, neuroglia include Schwann cells, satellite glial cells,...
Central Nervous System - Simply Psychology The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. Our brains have two primary functions, which are to control behavior and to regulate the body's physiological processes. ... Glial cells are non-neuronal cells in the CNS which do not themselves transmit messages but protect and support the neurons. Glia cells account ...
16.1 Neurons and Glial Cells – Concepts of Biology – 1st ... Glial cells of the (a) central nervous system include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglial cells. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons. Astrocytes provide nutrients to neurons, maintain their extracellular environment, and provide structural support. Microglia scavenge pathogens and dead cells.
Glial Cells - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Glial cells function as modulators of the CNS and PNS environments; they increase and decrease activity within the synapses by regulating neurotransmitter, oxygen, and ion uptake; they also aid nerve injury recovery. Specific roles are carried out by the different glial cell types.
Glial Cells | Location, Structure, Summary & Function The five types of glial cells found in the central nervous system are: Astrocytes Oligodendrocytes Microglia Ependymal cells Radial glia Glial cells are also found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes the nerves in the limbs that are not connected to the spine. There are two kinds of glial cells present there: Schwann cells






















Post a Comment for "41 label the glial cells of the cns"